
To control a PZT to achieve real-time auto-focusing, a Gaussian curve fitting method is used to process the spot information with the presented mathematical model giving the relationship between the detection value and the defocus value FES. The light reflected from the surface of the object reaches a CCD camera and forms a spot via a set of optical devices. The approach combines infrared light at a wavelength of 808nm with visible light. Here, a distance-measuring approach based on the laser triangulation principle is proposed with a corresponding mathematical model to overcome these problems and to satisfy the requirements of an industrial TFT-LCD (thin film transistor liquid crystal display) Inspection Microscope System in active auto-focus applications.
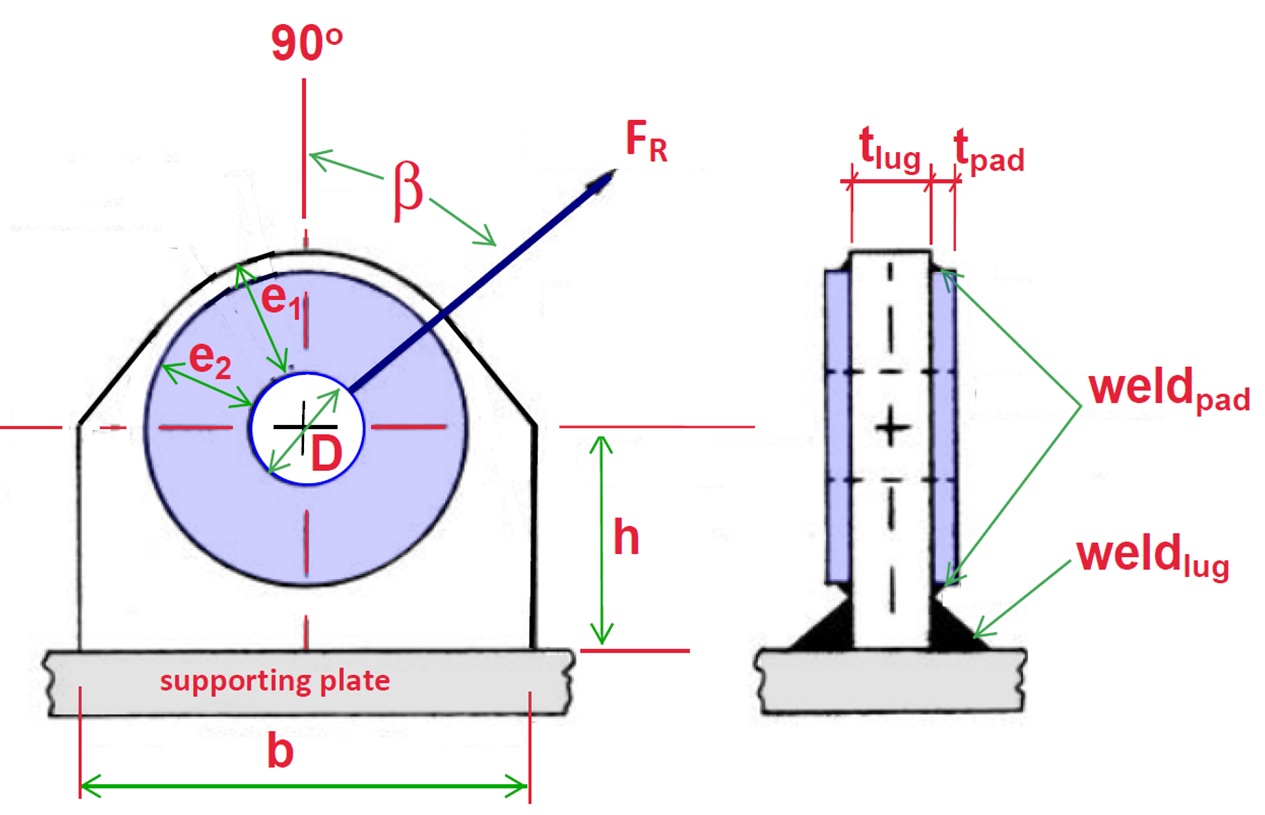
There are several common methods of analyzing a lug: Out of plane buckling ("dishing") - (not shown in the figure).Hoop tension failure / fracture on single plane.The numbers correspond with the labeled sections from the above figure: The failure modes for the lug are listed below.Limitations of the pinhole method and astigmatic defocus detection have difficulties in determining the direction of defocus and a restricted linear correction range. Simplified analysis - This method is based on first principles and involves making simplifying assumptions about the nature of the failure and calculating factors of safety. This has the advantage of being relatively easy, but it only gives an approximate determination of the adequacy of the lug.Īir Force Method - This method considers most of the failure modes above, and it uses empirical curves to determine more accurate allowable loads.

This method allows for lugs under axial loading, transverse loading, or oblique loading. This method also accounts for the interaction between the lug and the clevis pin.ĪSME BTH - This method considers most of the failure modes above, and it uses simplified equations with correction factors based on empirical data to determine more accurate allowable loads. This method is simpler than the Air Force Method, but it only allows for lugs under axial loading and does not account for the interaction between the lug and the clevis pin.Īll of these methods are described in the following sections.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
